Florida Pest Control Licensing And Recertification
|
|
Pomerix staff
Published: 2021-03-11
|
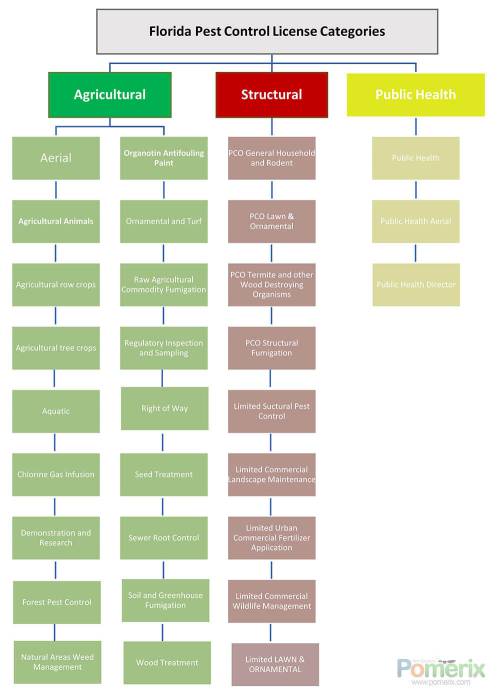
In Florida, all persons or entities who apply restricted-use pesticides (RUP) must own a pesticide applicator, pest control, or public health license. All Florida licenses can be divided into three main groups under agricultural, structural, or public health programs. Depending on the type of application, they may be further divided into private, public, and commercial subcategories.
License classifications:
- Private: An applicator who applies restricted-use pesticide on property owned or rented by the applicator or the applicator’s employer is considered a private applicator. Such a person must seek a private license under which the applicator is only allowed to apply RUP on their property.
- Public: An applicator who is employed by a federal, state, county, city, or other local agency or governmental entity who may use RUP on the job. The license is valid only for work performed for the governmental agency during the course of the employment.
- Commercial: An applicator who uses RUP for any purpose other than as given above for private and public applicator license. This license is needed for any company which offers pest control services to others.
Agricultural and related Pest Control
(Chapter 487, Florida Statutes)
Agricultural pest control refers to any pest management activity in areas where farming is performed, including where livestock is raised or where any ground crops, trees, or plants are grown. All persons who apply RUP to agricultural areas, industrial areas, and any outdoor areas must have a pesticide applicator license. This category does not include sites associated with buildings or public health pest control
- 487 core: General Standards Core exam covers basic pesticide application safety, including pesticide law, transporting, mixing, loading, storing, and disposing of pesticides, personal protective equipment, equipment calibration, pesticides in the environment, understanding labels, harmful effects, emergency response, and application procedure. This category is a prerequisite for obtaining a license in one of the categories below.
Agricultural Pest Control Categories:
- Aerial: This category refers to applicators applying RUP aerially as a public certification for ones who work for federal, state, county, or municipal public agencies or as commercial certification for contractors.
- Agricultural animals: This category refers to the applicators applying RUP to agricultural animals. Public or Commercial
- Agricultural row crops
: This category relates to applicators applying RUP to agricultural row crops or trees. Public or Commercial - Agricultural tree crops: This category refers to applicators applying RUP to agricultural tree crops. Public or Commercial
- Aquatic: This category refers to applicators applying RUP to any standing or running water, including banks or shorelines. Public or Commercial
- Chlorine Gas Infusion: This category refers to applicators who apply chlorine gas to treat water in residential pools with a portable system. Public or Commercial
- Demonstration and Research: This category refers to individuals applying RUP for research, including but not limited to extension specialists, county agents, commercial industry representatives, and other applications in public programs, and individuals who conduct field research that utilizes RUP. Public or Commercial
- Forest Pest Control: This category refers to persons applying RUP to forest sites. Public or Commercial
- Natural Areas Weed Management: This category refers to applicators using RUP to natural areas. Public or Commercial
- Organotin Antifouling Paint: This category refers to using organotin antifouling paints. Public or Commercial
- Ornamental and Turf: This category refers to the use of RUP to golf courses, athletic fields, parks, sod farms, and cemeteries. Public or Commercial
- Raw Agricultural Commodity Fumigation: This category refers to persons applying fumigant pesticides to raw agricultural commodities. Public or Commercial
- Regulatory Inspection and Sampling: Public or Commercial
- Regulatory Pest Control: For FDACS' Department of Plant Industry (DPI) employees who manage invasive species as a part of their job.
- Right-of-Way: This category refers to persons applying RUP in maintenance of roads, electronic lines, pipelines, railroads, and similar areas. Public or Commercial
- Seed Treatment: This category refers to persons applying RUP to seeds. Public or Commercial
- Sewer Root Control: This category refers to persons applying RUP to control or prevent the growth of roots in sewer lines or pipes. Public or Commercial
- Soil and Greenhouse Fumigation: This category refers to persons applying restricted use soil and greenhouse fumigants. Public or Commercial
- Wood Treatment: applying wood preservative pesticides or other RUPs in wood treatment facilities to produce treated wood products. Public or Commercial
Structural Pest Control
(Chapter 482, Florida Statutes)
According to Chapter 482, Florida Statutes, the Structural Pest Control Industry certification regulates any person who applies pesticide routinely in private or public structures. However, structural pest control should not be confused with agricultural (487) and mosquito control (388).
- 482 Core: The core category is a generalized area that can apply to ALL STRUCTURAL pesticide uses or applications and is a prerequisite for obtaining a license in one of the categories below.
Structural pest control license categories:
- Limited Certifications: For private and governmental pest control
- Limited Commercial Landscape Maintenance: This license is for landscape maintenance contractors applying pesticides to their customer’s property which is sometimes referred to as a "Round-Up" license. It also allows the licensed applicator to use herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides to ornamental plant beds and shrubs. Products are limited to "Caution" labels only. Turf areas and stormwater ponds are off-limits. Only backpack sprayers having no more than a 5-gallon capacity and handheld 3-gallon compressed air “pump-up” sprayers are allowed, and powered equipment is prohibited. Each individual applicator must be licensed.
- Limited Lawn and Ornamental: This license is only for employees applying pesticides to their employer's property or employees of government agencies who apply pesticides to the turf & ornamental areas. Powered equipment is allowed, and each applicator must be licensed.
- Limited Structural Pest Control: This type is only applicable for government employees who apply pesticides in, on, or under structures belonging to the government; persons who apply pesticides in, on, or under structures on their own private (business) property; and employees who apply pesticides in, on, or under structures on private (business) property owned by their employers
- Limited Urban Commercial Fertilizer Application: This license is required for commercial fertilizer applicators to use fertilizer to urban properties. It does not include any other type of pesticide applications (such as weed-n-feed products) to turf or ornamental areas (a separate pesticide license is required). Each applicator must be licensed.
- Limited Commercial Wildlife Management: This license is required for commercial wildlife trappers to exclude and trap (including glue boards) commensal rodents in, on, or under structures. However, it does not allow wildlife management workers to make any pesticide applications. Structures can be residential, governmental, or commercial structures such as homes, schools, municipal/agency offices, banks, grocery stores, apartments, common condominium areas, hotels, and restaurants.
- Operator Licenses: For the owner of pest control company
- PCO Lawn & Ornamental: This license allows the applicator to apply herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides to lawn & ornamentals. Restricted use products may also be used, and applications may be made to plant beds, shrubs, and turfgrass. Also, powered equipment is allowed. May supervise pesticide applications performed by "Pest Control Identification Card" holders
- PCO General Household Pest and Rodent Control: This license allows the applicator to use pest control in any structure except for fumigation and termites, and other wood-destroying organisms. This category includes control of cockroaches, fleas, spiders, rats, and mice, and other species inside buildings. Also, powered equipment is allowed. May supervise pesticide applications performed by "Pest Control Identification Card" holders.
- PCO Termite and Other Wood-Destroying Organisms Control: This license allows the applicator to control termites or other wood-destroying organisms, including fungi, through chemical or mechanical methods, such as moisture control for preventing or controlling fungus in structures. However, it excludes fumigation or general household pest control.
- PCO Structural Fumigation: This license allows the applicator to apply a fumigant inside an enclosed space or in or under a structure or tarpaulin in concentrations that may be hazardous to people.
* Bee Eradication or Removal: This is not a license category. However, the Bureau of Entomology and Pest Control, regulates ALL METHODS of pest control under Chapter 482, Florida Statutes (FS). Eradication of pests (including honeybees) meets the definition of pest control, Chapter 482.021, Florida Statutes. Therefore, a person hired to eradicate a bee nest or swarm (even if they don't "spray") must possess either a General Household Pest (GHP) license for indoor and outdoor removal or a Lawn and Ornamental license (L&O) for removal of outdoor colonies or swarms only such as in a tree. Nevertheless, a registered beekeeper (with the Department’s Division of Plant Industry) can also remove the colony with non-lethal methods as per rule 5E-14.151, Florida Administrative Code (FAC).
Public Health Pest Control
(Chapter 388, Florida Statutes)
According to chapter 388, Florida Statutes, pesticide applications made for area-wide mosquito control or control of other arthropods of public health significance, namely midges, dog files, house files, yellow files, and sand files, require a public health pesticide applicator license.
Core: General Standards Core exam covers basic pesticide application safety, including pesticide law, transporting, mixing, loading, storing, and disposing of pesticides, personal protective equipment, equipment calibration, and pesticides in the environment, understanding labels, harmful effects, emergency response, and application procedure.
Categories:
- Public Health: This license is required for persons who apply pesticides to control arthropods of public health importance. It is also necessary for government entities to make widespread community or municipal mosquito-control applications over a large area, and pest control companies contracted to perform mosquito control activities for a government agency or mosquito control district. Businesses which install automated mosquito misting devices or offer residential or commercial fogging and barrier treatments to clients must obtain a license. They must also have a pest control operator certified in General Household Pest Control or Lawn and Ornamental Pest Control.
- Public Health Aerial: This category refers to persons who apply pesticides aerially to control public-health pests such as mosquitoes and biting flies.
- Public health Director: This category refers to individuals applying for a position as a director of a mosquito control district or a county program for mosquito control. They must obtain a license before employment or within six months of employment in this role.